- Česky (cs)
- English (en)
Reference interface of public administration
Description of the reference interface
In accordance with its definition enshrined in Act No. 365/2000 Coll., on public administration information systems and Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on basic registers, the reference interface is effectively understood as an interface for the implementation of links between public administration information systems, especially in the implementation of an interconnected data fund by sharing data between individual agency information systems in the form of shared services. The reference interface is therefore a communication interface for the provision and use of shared services of individual administrators of public administration information systems.
The reference interface consists of three main components:
| Component | Abbreviation | Functionality description |
|---|---|---|
| Information system of basic registers | ISZR | Provides all services related to the use of data from basic registers, also implements services for editors to the registers and for sharing data of editors of registers |
| Information Shared Service System | eGSB/ISSS | Interface for sharing and exchanging data between ISVS and making links between them |
| Information system for bulk data output in multiagenda queries (Forms Agenda Information System) | FAIS | It is used for processing queries and outputting data in the form of forms, including bulk forms, also from multiple PIs or other ISVS. Queries and outputs are transmitted via Data Mailboxes. |
The use of data via the reference interface is always made exclusively on the basis of the relevant permissions recorded in RPP, but this does not mean that RPP controls the actual release of data. The final decision on whether or not to release data is always the responsibility of the source AIS (the one whose data is requested). It makes this decision on the basis of the entitlement reference data recorded in RPP. In the future development of PPDF, it is envisaged that permissions for data or specific services will be checked by ISZR and eGSB/ISSS using reference data from RPP. Thus, the end state should be that the requesting system calling the service receives the requested data or information that it does not have the necessary permissions for the request. Thus, permissions, and thus access to data and services, would not need to be done by the system or its administrator, but would be controlled by the RPP references.
Through the reference interface:
- The writing and editing of data in the basic registers is implemented.
- Perform Basic registry editors using the services of the external interface ISZR
- Executes the use of basic registers data
- Notification and update services for basic registers are also implemented using the ISZR external interface services
- Data exchange in the form of shared services between AIS is implemented
- Implement bulk data output and query/response composition services for multiple data
- Implemented by the FAIS component and used by OVM or SPUU with appropriate authorization
- FAIS makes calls to the ISZR and ISSS services based on a request received via the data mailbox and returns the compiled response to the requester again via the data mailbox
- Implement notification and data update services in individual agendas using the central component
Basic rules for using the reference interface
- Comply with the Decree on Act 365/2000 Coll., especially on the technical and functional parameters of the connection to the reference interface
- The reference interface is accessed by the OVM through its AIS and by the SPÚ through the private data use system or through the AIS of another OVM
- Each system accessing the reference interface must prove its 'identity' by means of a system certificate issued by a Certification Authority under the management of SZR
- When exchanging data on subjects of law or objects of territorial identification, it is verified whether these subjects (ROB, ROS) or objects (RÚIAN, RPP) are listed in the basic registers (verification of the reference link)
- The OVM requesting data on a specific subject is responsible for its proper identification in its agenda, i.e. the indication of the AIFO if it is a natural person or the ID number if it is a legal person. If the subject is not properly identified, the data obtained may be indicative only
- Records (logs) of the identification of the requesting system, time of response, structure and content of the data provided shall be kept by the providing system. The identification of the providing system, time of response, structure and content of the data shall be kept by the receiving system. The reference interface shall record the identification of both systems, the time and the structure of the data transmitted.
- Procedural interfacing with eSSL when the reference interface is used to transmit documents according to the rules of the file service. This only applies to situations where the content is actually a document and therefore not just a data transfer.
Information system for the management of the use and publication of data of the Public Administration Reference Interface of the Czech Republic
The Information System for the Management of the Extraction and Publication of the Data of the Public Administration Reference Interface of the Czech Republic (also referred to as the "Connection Management System") is a Public Administration Information System that enables any entity that is connected to the Public Administration Reference Interface (according to Act 365/2000 Coll.) to manage data on information systems that provide or extract data through the Reference Interface. The link management system will be created as an extension of the current RAZR system (registration authority of basic registers) or as a new system and must support the following functionalities:
- Login via JIP/KAAS
- Login via the NIA system
- Evidence of all connected IS (agency information systems and private data use systems) according to the register of public administration information systems
- Evidence of all subject administrators of connected IS and their administrators (editors)
- Evidence of all contexts according to the agendas defined in the RPP
- Control of data permissions according to RPP
- History of data consumption and publication of the connected IS according to the logs of the reference interface
- Individualization of information for logged-in and authorized user
- Allowing reporting of unauthorised drawdown/data provision, including tracking of progress
- Allow reporting of certificate misuse, including tracking of progress
- Enable ordering a new certificate, including progress tracking
- Enable context management (creation, modification, deletion)
Basic Registry Information System
The Information System of Basic Registers is legislatively enshrined in Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on Basic Registers. The ISZR is a public administration information system through which data sharing between individual basic registers, basic registers and agency information systems and agency information systems with each other, management of data access permissions and other activities are ensured.
The ISZR consists of two basic interfaces:
| Interfaces | Main users | Functionality description |
|---|---|---|
| Internal interface services | Only the ISZR in relation to the basic registers | Internal services that can only be used by the ISZR to retrieve and dereference data from the individual basic registers |
| External interface services | Agenda information systems | Services enabling the use of data from basic registers and basic register editors |
In particular, the following are implemented through the ISZR:
- Access to data held in the basic registers
- Services of claiming, contesting, notification, updating data from basic registers
- Entry and modification of data in the basic registers
- Translation of agency identifiers of natural persons
- Ensuring compliance with authorisations recorded in the Register of Rights and Obligations
Users follow the table below to connect to the basic registers:
| User | Path | Ensures |
|---|---|---|
| Subject of the right | cannot access directly, indirectly through citizen's portal or universal contact points and extracts from it | |
| The public authority | shall ensure the management of the basic registers by its Agenda Information System | after the conditions |
| public authority | by the Agenda Information System of another administrator | shall be provided by the administrator of the AIS in question |
| Public authority | through the CzechPOINT@office interface | will be provided by the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic, the CzechPOINT@office administrator in cooperation with the local administrator |
| Private legal user of data | Through the Agenda Information System built by the OVM | shall be provided by the OVM that administers the respective AIS |
| Private data user | Private data exploitation system | To be provided by the PSO authorised to operate such a system |
In order to connect the agency information systems to the basic registers, certain basic conditions must be fulfilled, which are laid down by the Administration of the basic registers in its operational documentation of the ISZR. In particular:
- The AIS administrator must have its IS declared in the ISVS register in the Register of Rights and Obligations
- It must have declared in the RPP the competence in the agenda(s) it will perform with this AIS for the relevant OVM
- The AIS administrator must indicate in the RPP which OVMs/SPMUs can access the RO or other AISs via its AIS.
- The AIS must be connected to the relevant access point (KIVS or Internet). The method and process of connecting the AIS to the KIVS is outside the scope of the RoW system
- The AIS must be certified to access the eGON interface. Certification is a process within the competence of SZR. Within this process, the scope of the AIS - agenda, agency roles and OVM - is defined. This process is described in a separate document available on the SZR website.
- The AIS must be issued with an electronic client certificate. Issuing a client certificate is the last step in the AIS certification process, which is carried out by SZR
- The AIS must be allowed access to specific eGON services within the RAZR (Registration Authority of the RoW) according to the security profile. Permissions to individual data are defined based on the OVM / agenda / agenda role combination, and are derived from the information in the RPP
- Must have implemented calls to the eGIS services in its AIS, or be able to properly call, consume and use the web services of the eGIS external interface according to the eGIS operational documentation
Catalogue of ISZR eGON services
An always up-to-date list of eGON services is available on the SZR website Catalogue of eGON services. The list here is valid until the end of 2020.
The individual eGON services are divided into main categories:
- Services based on basic registries
- ROB-based services
- ROS-based services
- RUIAN-based services
- RPP-based services
- ORG-based services
- Services based on ISZR
- Services based on AIS - so-called composite services
In addition to the above mentioned catalogue and list of services, there are 2 specific services categorized as composite services whose output relates to the photos and biometric signatures of electronic ID cards and passports
| AIS-based services - composite services | E197 - agendaMediaDataCtiAifo.docx | 01.03 | 26.09.2017 |
| E198 - agendaMediaDataCtiPodleUdaju.docx | 01.03 | 26.09.2017 |
Basic registers
Base registries are the basic (reference) data source of data on subjects and objects of law and on the performance of public administration.
These are reference data on
- natural persons,
- legal entities,
- addresses and territorial elements and real estate
- public authorities and private data users,
- agendas and scope of public administration,
- certain decisions amending reference data.
For more information on reference data, see Reference data.
The base registries thus form the backbone of an interconnected public administration data fund, including a mechanism for pseudonymisation and linking identifications from individual agencies. In addition, they provide individuals in particular with an overview of the use of their data by individual readers (OVM, SPUU, etc.) and the provision to others.
Register of inhabitants (ROB)
The Population Register is a basic register according to Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on basic registers, which records reference data on natural persons. The administrator of the Population Register is the Ministry of the Interior. The primary editors are the individual OVMs through the Information System for Population Registration and Agenda Information System for Foreigners.
The subjects of the data recorded in the population register are
- citizens of the Czech Republic,
- foreigners who reside in the territory of the Czech Republic as permanent residents or on the basis of a long-term visa or long-term residence permit,
- citizens of other Member States of the European Union, citizens of States bound by an international treaty negotiated with the European Community, citizens of States bound by the European Economic Area Treaty and their family members who reside in the territory of the Czech Republic as part of their permanent residence or who have been issued with a document of temporary residence in the territory of the Czech Republic for more than 3 months,
- foreigners who have been granted international protection in the form of asylum or subsidiary protection in the Czech Republic,
The reference data on natural persons are1):
- surname, maiden name
- first name, where appropriate,
- gender,
- the address of the place of residence, or, where applicable, the address to which documents are to be served in accordance with another legal regulation; these addresses are kept in the form of a reference link (address place code) to the address reference in the territorial identification register; in the case of an address to which documents are to be served pursuant to another legal regulation, the identification of a post box or a delivery box or an address which is outside the territory of the Czech Republic and which has not been assigned an address place code in the territorial identification register is also recorded; in the case of an address of a place of residence, this information is marked as the address of the office if it is marked in the same way in the information system of the population register or the information system of foreigners,
- the date, place and district of birth, in the case of a subject of law who was born abroad, the date, place and state where he was born; the information on the place and district of birth on the territory of the Czech Republic is kept in the form of a reference link (territorial element code) to the reference in the territorial identification register,
- the date, place and district of death, if the death of the subject of the right is outside the territory of the Czech Republic, the date of death, the place and the State in whose territory the death occurred; if a court decision is issued declaring the subject of the right to be dead, the date indicated in the decision as the date of death, or as the date on which he/she did not survive, and the date on which the decision became final shall be entered; the place and district of death in the territory of the Czech Republic shall be entered in the form of a reference link (territorial element code) to the reference entry in the territorial identification register,
- nationality, or multiple nationalities, if applicable,
- limitation of legal capacity,
- marital status or registered partnership,
- numbers and types of identification documents and their expiry date,
- the type of data box and the identifier of the data box, if this data box is accessible.
Non-reference data is also kept on natural persons in the population register:
- a telephone number for the public mobile telephone network or an e-mail address for sending a selected range of information,
- serial number, issuer and validity of the qualified certificate for electronic signature.
- Personal security code, which is authentication data for the purposes of the population register. It is kept in encrypted form and is non-public
- Agenda identifier of the natural person, which is the identifier for the population register agenda
The population register also holds operational data
- a record of the use of population register data for the purposes of agency information systems,
- a record of the disclosure of data to the subject of the right or to another person, which includes the date and time of the disclosure, an identifier of the consent of the subject of the right to disclose the data to another natural or legal person and the identification of the person who disclosed the data,
- the date of the last change to each entry in the population register,
- a record of the granting or withdrawal of the right holder's consent to disclose the data to another natural or legal person.
The data editors are:
- In the case of citizens of the Czech Republic, the editor is the Ministry of the Interior, which records the data through the agency information system for population registration and the agency information system for identity cards and the agency information system for travel documents.
- For foreigners, the editor is the Police of the Czech Republic or the Ministry of the Interior, which record data through the agenda information system for foreigners.
- For data boxes, the editor is the Ministry of the Interior as the administrator of the Information System of Data Boxes.
- The editor of operational data is the Basic Registers Administration through the Basic Registers Information System
Register of legal persons (ROS)
The register of legal persons is a basic register according to Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on basic registers, which records reference data. The administrator of the register of persons is the Czech Statistical Office. The primary editors are authorities and institutions that are already legally obliged to register persons. These include the Commercial Register, the Trade Register, registers or information systems of selected ministries and central government bodies, professional chambers, municipalities, regions, etc. The Ministry of the Interior with the Data Box System (ISDS) is the secondary editor.
The subjects of the data kept in the register of persons are:
- legal entity,
- organisational unit and organisational unit of a legal person,
- organisational unit of the State,
- an internal organisational unit of an organisational unit of the State, if this internal organisational unit is entrusted by law with its own competence,
- an entrepreneurial natural person,
- a foreign person and an organisational unit of a foreign person,
- a trust fund, if they are entered in the register pursuant to this Act or another legal regulation.
The reference data on legal persons are:
- business name or designation or name, if applicable, and surname, if the natural person engaged in business is not registered in the Commercial Register,
- the name or, where applicable, the first and last names of the natural person engaged in business or of the foreign person and the organisational unit of the foreign person; if the person is entered in the population register, this data shall be kept in the form of a reference link (agency identifier of the natural person) to the reference entry in the population register,
- the agenda identifier of the natural person for the agenda of the register of persons,
- person identification number,
- date of creation or date of registration under other legislation,
- date of termination or date of deletion from the register under other legislation,
- legal form,
- type of data box and identifier of the data box, if this data box is accessible,
- the statutory body, expressed by reference to the population register or the register of persons or by the name, surname and residence of a natural person or the name and registered office of a legal person, if these persons are not entered in the population register or the register of persons,
- the liquidator, expressed by reference to the population register or the register of persons, or by reference to the name, surname and residence of a natural person, if applicable, or to the name and registered office of a legal person, if these persons are not entered in the population register or the register of persons,
- the guardian of a legal person, expressed by reference to the population register or the register of persons, or by reference to the name, surname and residence of a natural person, if applicable, or to the name and registered office of a legal person, if these persons are not entered in the population register or the register of persons,
- the insolvency administrator, expressed by reference to the population register or the register of persons, or the name, surname and residence of a natural person or the name and registered office of a legal person, where these persons are not entered in the population register or the register of persons,
- a receiver expressed by reference to the population register or by the name, surname and residence, where applicable, of the person concerned, if that person is not entered in the population register,
- legal status,
- the address of the person's registered office; if the building is a building recorded in the territorial identification register, this information shall be recorded in the form of a reference link (address location code) to the address reference in the territorial identification register,
- date of commencement of the activity at the establishment,
- the identification number of the establishment,
- the date of cessation of the activity at the establishment,
- the address of the place of establishment; where the building is a building recorded in the territorial identification register, this information shall be entered in the form of a reference link (address place code) to the address reference in the territorial identification register,
- the address of the place of residence in the Czech Republic in the form of a reference link (address place code) to the reference data on the address in the register of territorial identification, or the residence abroad of a natural person, a foreign person and an organisational unit of a foreign person; in the case of persons entered in the register of residents, the address of the place of residence in the form of a reference link (code of the agency identifier of a natural person) to the reference data on the natural person in the register of residents,
- interruption or suspension of activities under another legal provision; in the case of activities corresponding to one agenda, the interruption of all such activities.
Non-reference data on legal persons shall also be kept in the register of persons:
- a telephone number for the public mobile telephone network or an e-mail address for sending a selected range of information.
Operational data shall also be kept in the register of persons:
- agenda code,
- editor's personal identification number,
- date of initial entry in the register of persons,
- date of the last change to the data recorded in the register of persons,
- record of the use of the data from the register of persons.
Data editors are:
| Person Name | Person Type | Agenda^ROS Editor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attorneys | FO | A8 | Czech Bar Association |
| Employment Agencies | FO | A531 | Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs |
| Accredited person under the Consumer Credit Act | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Auditors | FO | A6 | Chamber of Auditors of the Czech Republic |
| Road Safety Auditors | FO | A1381 | Ministry of Transport |
| Authorized Architects | FO | A54 | Czech Chamber of Architects |
| Authorised Engineers and Technicians | FO | A54 | Czech Chamber of Chartered Engineers and Technicians active in Construction |
| Churches and religious societies | PO | A5 | Ministry of Culture |
| Czech National Bank, Czech Television, Czech Radio, Regional Council of the Cohesion Region, General Health Insurance Company | PO | A325 | Ministry of the Interior |
| Tax Advisers | FO | A7 | Chamber of Tax Advisers of the Czech Republic |
| Voluntary associations of municipalities | PO | A343 | Locally competent regional authority or the Municipality of the capital city Prague |
| License holders for business in energy sectors | FO | A684 | Energy Regulatory Authority |
| European Groupings for Territorial Cooperation | PO | A561 | Ministry for Regional Development |
| Natural Persons - Operators of Postal Services | FO | A926 | Czech Telecommunications Office |
| Persons operating a trade (sole traders) | FO | A121 | Locally competent trade licensing authority |
| Private associations | PO | A943 | Locally competent municipality with extended competence, Ministry of Agriculture |
| Insolvency practitioners | FO | A1901 | Ministry of Justice |
| Investment intermediaries | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Communal Contributory Organisations | PO | A388 | Counties, Municipalities |
| Mediators | FO | A1461 | Ministry of Justice |
| International military organisations established on the basis of an international treaty | PO | A5517 | Ministry of Defence |
| Foundations and endowments | PO | A120 | Registrar's court with local jurisdiction |
| Notaries | FO | A484 | Notary Chamber of the Czech Republic |
| Public Benefit Corporations | PO | A120 | Local Registry Court |
| Commercial companies; cooperatives, business units, other persons registered in the Commercial Register | PO | A120 | Locally competent court of registration |
| Trade unions and employers' organizations, affiliated trade unions and employers' organizations, international trade unions, international employers' organizations, affiliated international trade unions, affiliated international employers' organizations | PO | A120 | Locally competent court of registration |
| Organizational units of the State | PO | A325 | Ministry of the Interior |
| Persons handling high-risk biological agents and toxins | FO | A914 | State Office for Nuclear Safety |
| Persons carrying out mining and mining-related activities | FO | A4293 | Czech Mining Authority |
| Persons involved in the production and distribution of pharmaceuticals | FO | A1243 | State Institute for Drug Control |
| Persons authorised for exchange and foreign exchange activities | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Persons using nuclear energy and ionizing radiation | FO | A3905 | State Office for Nuclear Safety |
| Patent Attorneys | FO | A31 | Chamber of Patent Attorneys of the Czech Republic |
| Entrepreneurs in Electronic Communications | FO | A304 | Czech Telecommunications Office |
| Insurance intermediaries | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Political Parties and Political Movements | PO | A3 | Ministry of the Interior |
| Audiovisual Media Service Providers | FO | A1138 | Radio and Television Broadcasting Council |
| Providers of small-scale payment services | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Healthcare service providers | FO | A1086 | Locally competent regional authority or the Capital City Municipality Prague |
| Providers of social services | FO | A530 | Locally competent regional authority or the Municipality of Prague Prague |
| Aircraft work operators and airport operators | FO | A575 | Civil Aviation Authority |
| Operators of professional veterinary activities | FO | A1044 | State Veterinary Administration |
| Radio and Television Broadcasting Operators | FO | A453 | Radio and Television Broadcasting Council |
| Operators of emission measurement stations | FO | A998 | Locally competent municipality with extended competence |
| Operators of technical inspection stations | FO | A998 | Locally competent regional authority or Capital City Council Prague |
| Zoo operators | FO | A696 | Ministry of the Environment |
| Restaurators | FO | A434 | Ministry of Culture |
| Separate insurance claims adjusters | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Separate consumer credit intermediary | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Court Executors | FO | A479 | Executors' Chamber of the Czech Republic |
| Court Experts and Interpreters | FO | A481 | County Courts, City Court Prague |
| Community of unit owners | PO | A120 | Locally competent registration court |
| Clubs (formerly civic associations), affiliated associations (formerly an organisational unit of a civic association) | PO | A120 | Registration court with local jurisdiction |
| State Funds | PO | A325 | Ministry of the Interior |
| State Contributory Organisations | PO | A24 | Ministries and other Central Administrative Authorities |
| Trust Funds | PO | A4047 | Locally competent court of registration |
| School legal entities | PO | A676 | Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports |
| Institute | PO | A120 | Locally competent court of registration |
| Consumer Credit Act tied representative | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Public and State Universities | PO | A325 | Ministry of the Interior |
| Public research institutions | PO | A4 | Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports |
| Public corporations - region, municipality, capital city of Prague | PO | A325 | Ministry of the Interior |
| Veterinarians authorized to perform veterinary medical and preventive activities | FO | A636 | Chamber of Veterinary Surgeons of the Czech Republic |
| Foreign legal entity, branch plant of a foreign legal entity, branch plant of a foreign natural person | PO | A120 | Locally competent registration court |
| Foreign association, foreign branch association | PO | A120 | Locally competent registry court |
| Interest association of legal persons | PO | A120 | Locally competent court of registration |
| Representative Office of a Foreign Bank | PO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Agricultural Entrepreneurs | FO | A944 | Ministry of Agriculture |
| Consumer credit intermediary | FO | A11 | Czech National Bank |
| Special organization for representation of Czech interests in international NGOs, organizational unit of special organization for representation of Czech interests in international NGOs, international NGO, organizational unit of international NGO | PO | A120 | Locally competent court of registration |
For non-referential data, the editor is the Czech Statistical Office.
Register of Territorial Identification of Addresses and Real Estate (RÚIAN)
The Register of Territorial Identification of Addresses and Real Estate is a basic register according to Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on Basic Registers, which records basic territorial elements and addresses. The administrator of the Register of Territorial Identification is the Czech Geodetic and Cadastral Office. The primary editors are cadastral offices, through the cadastre information system, building authorities through the territorial identification information system, municipalities and the Czech Statistical Office.
The Register of Territorial Identification contains data on the following basic territorial elements:
- the territory of the state,
- the territory of a cohesion region according to another legal regulation,
- the territory of a higher territorial self-government unit,
- the territory of a region,
- the territory of a district,
- administrative district of a municipality with extended competence,
- the administrative district of a municipality with a designated municipal authority,
- territory of a municipality,
- the territory of a military district,
- administrative district in the capital city of Prague,
- the territory of a municipal district in the capital city of Prague,
- the territory of an urban district in the capital city of Prague,
- the territory of an urban district and an urban part of a zoned statutory city,
- cadastral territory,
- the territory of a basic settlement unit,
- building object,
- address place,
- land in the form of a parcel of land
The register of territorial identification shall also contain data on special purpose territorial elements by means of which the territory is expressed by another legal regulation, if another legal regulation provides that such data shall be entered in the register of territorial identification and if these special purpose territorial elements are entirely composed of at least some of the basic territorial elements.
The territorial identification register shall also contain data on the following territorial registration units
- part of a municipality
- a street or other public space
The reference data in the territorial identification register are:
- identification data,
- data on links to other territorial elements or territorial registration units,
- data on the type and use of the land and its technical and economic attributes,
- data on the type and use of the building object,
- data on the type and method of protection of the property,
- addresses,
- locational data of cadastral areas and superior elements,
- locational data of territorial elements and territorial registration units - only in those cadastral territories where the cadastral map is kept in digital form.
Register of Rights and Obligations (RPP)
The Register of Rights and Duties is administered by the Ministry of the Interior and contains information for controlling access to the data of other basic registers; at the same time, this register provides a basic overview of the agendas carried out by public authorities; information on citizens and legal entities is kept in this register on decisions that have led to changes in the data in the basic registers. In addition, the RPP serves as a source of information for ISZR in managing user access to data in individual registers and agency information systems. This means that whenever a given subject attempts to obtain a certain data or even to change (edit) it, the system assesses whether the subject will be allowed to work with the data provided by the public administration on the basis of legal authorization, and thus the RPP becomes an important component of the ZR within the concept of using the interconnected data pool and data sharing across not only the state administration for the management of public administration performance. The RPP includes in particular:
- Public administration agencies and their responsibilities
- List of Public Authorities and private users of data from basic registers
- A map of the competences of public authorities within the agenda model
- Details of data held in the Agendas and their provision and use
- Data on the entitlements of public authorities and private users to access data from basic registers and agency information systems
- Decisions on the basis of which reference data in the Population Register and the Register of Persons are changed
- List of public administration information systems and their relation to agendas and data held in them
The RPP also includes the technical structure of the data, the description of which is set out in the Decree on Act 111/2009 Coll. Important from the development perspective is the addition of a reference to the codebook, i.e. the dataset published in the public data fund within the National Catalogue of Open Data.
- Directory: a reference to a dataset representing a directory published in the National Catalogue of Open Data according to the rules of Public Data Fund. If the data is created in the agenda, it is a reference that says the data is the source of the codebook, if it is a downloaded data, it is a reference to a codebook published by another entity.
The administrator of the Register of Rights and Duties is the Ministry of the Interior, the primary editors are the notifiers of public administration agendas.
The basic elements for agendovy model of public administration are maintained in the RPP. There is also a map of the shareable data of each agency and technical information about the data held within each agency and the permissions to access the data.
Another part of the RPP is a record of public administration information systems, their link to the agendas, data on their administrators, etc.
The methodology for recording VS services, their actions and the digitisation plan is given in here.
Key roles in relation to basic registers
The following roles are defined in relation to the use of base registries and are referred to as such in this document:
| Roles | Description and Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Administrator of the basic register | Public authority that manages the relevant basic register | For ROB and RPP it is the Ministry of Interior, for ROS it is the CSO, for RÚIAN it is the ČÚZK |
| Editor of reference data | Public authority which by law carries out the editing and recording of reference data and is therefore responsible for its correctness and is obliged to deal with complaints and data updates | For ROB it is the Ministry of Interior (e.g. through registration offices and registry offices), for ROS and RÚIAN it is the individual agency points according to the respective laws |
| User of reference data (reader) | Public authority or private user, who is obliged or authorised to use reference data and accesses the RO for this purpose | Individual OVMs operating in agencies, AIS administrators, data subjects themselves |
| Right holder | Specific natural or legal person about whom data are kept in the registers | Any natural or legal person for their data. A legal person is always linked to a natural person. |
| Announcer of the agenda | Announcer of the agenda kept in the RPP (see Agendovy model of public administration) | For the registry agenda the Ministry of Interior, for the health services agenda the Ministry of Health, for the pensions agenda the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs |
| Authority acting in the agenda | Public authority which by law exercises competence in the agenda (see Agendovy model veřejnéne_spravy) |
Reference data
Reference data are data held in the base register that are marked as reference. It is a general legal and procedural premise that reference data are considered valid in the exercise of public administration unless proven otherwise or unless they are challenged by the relevant editor.
It is therefore the case that the public administration must act on the basis of these reference data and, conversely, that if the public administration acts on the basis of these reference data, there can be no maladministration due to inconsistency with the facts.
Entering and editing reference data
The editing and recording of reference data is always the responsibility of the editor responsible. The distinction of the editor's responsibility is not only per subject, but also per data. There is also a situation where there is more than one editor per subject. In this case, the editors are divided into primary and secondary editors. The primary editor is responsible for the actual existence of the entire record (including creation, update and deletion), whereas the secondary editor is responsible only for the individual entity data (including updates). A typical example of a situation of a primary and a secondary editor are legal entities, where the relevant primary editor is responsible for the creation and registration of the relevant basic data (the court of registration, the regional office, the trade department of the municipality, etc.) and the secondary editor (the Ministry of the Interior as the ISDS administrator) is responsible for the additional data, e.g. on the data box. Therefore, the secondary editor cannot establish or cancel the entity, but only adds additional data to it.
The basic duties of the editor are therefore:
- To write and edit data on the basis of the procedural execution of the agenda, which determines whether there is a document registered in the filing service to be executed
- To deal with the complaints process, including challenges to the accuracy of data from the keeper of the basic register, the editor himself or any public authority
- Address the accuracy and timeliness of the data
The documents on the basis of which the editor has carried out his duties must follow document_management.
Virtual Reference Data
Virtual reference data are those data that are created by deriving, merging or otherwise modifying existing reference data. They therefore do not meet some of the requirements of traditional reference data, such as the responsibility of a specific editor. Virtual reference data have a label, a definition and a described process for how they are created in each specific service that can provide them. A typical example would be the virtual reference data "full name", which is composed of the reference data "first name or first names" and "last name". Other such virtual data may be:
- Age
- Name without diacritics
- Address in uppercase only
- Number of days until expiration of identification document
- Telephone number in international format
- etc.
Virtual reference data need not be explicitly mentioned in the law as content of a specific basic registry, as they are created and extinguished with the call of a given ISZR or ISSS service. They are therefore only the content of the service description.
Currently, no ISZR or ISSS service has the capability to provide a virtual reference. This functionality is foreseen in the development of the PPDF.
Indicator data type
An indicator is a reference data held in the basic register which serves to indicate that potentially relevant data on an entity are held in other information systems. The purpose of indicator data is to prevent unnecessary queries to information systems where such information is not held.
The administrator of the basic register is responsible for the allowed set of indicators, including their names.
The editor of the indicator data type is the administrator of the information system that maintains the indicated data, which are entered into the basic register in the same way as the reference data, i.e. by automatic processes. An indicator may also be a virtual data of the basic register and multiple indicators may relate to one subject.
The indicator data type has the following basic attributes:
- name - the unique name of the indicator, example: COVID-19,
- AIS identifier + agenda identifier,
- optional context identifier, within which detailed data can be retrieved via ISSS,
- Unnumbered list optional refinement code,
- optional text refinement.
The indicator type data contains other standard attributes:
- validity start date and time,
- expiry date and time,
- date and time of initial entry,
- date and time of last change,
- status (S, N, X, F).
Currently no ISZR or ISSS service has the capability to provide an indicator. This functionality is foreseen in the development of the PPDF, where the following modifications are required to introduce this data:
- Add a text item ListIndicator, a string type, and write and read structures to AuthorizationInfo. The names of the flags to be returned/written are entered into the ListIndicator. It is the equivalent of a ListIndicator, and ISZR checks that the querying AIS has permission to read or write to a particular indicator.
- Access to data of type Indicator is controlled by the Registry of Rights and Responsibilities in the standard way. A user (OVM, agenda, activity role) must be allowed to access an indicator with a given name.
- Adding a new indicator must not require XSD modifications or even a new agenda declaration to be as operational as possible.
Data Accuracy Claim Process
The data accuracy complaint process can be initiated by anyone who has doubts about the accuracy of the data. The process itself is then always handled by the primary source of the data - i.e. its editor. The process starts with the receipt of a message that contains a doubt about the correctness of the data (from another OVM, a legal entity, a registry administrator, etc.). The editor is then obliged to mark the data in question as questionable. Subsequently, the editor of the data must perform a validation of its correctness, which may result in the closure of the complaint as unjustified (and thus preserving the value of the data) or justified (and thus changing it to the correct value). At the same time as closing the claim, it removes the doubt from the data. The claim process itself is governed by the Administrative Procedure Code.
Use of reference data
Each public authority is obliged to use reference data from the basic registers to the extent determined by its competence in the respective agenda. It does so either by using the services of ISZR and linking its agency information systems or by using one of the other tools of the Reference interface.
The basic obligations of the OVM and the SPUU using the data are therefore:
- Use reference data in the agendas
- Use up-to-date reference data, which can be ensured by one of the following two, but always in accordance with the ISZR operational documentation:
- By using the mechanism of notification of changes to reference data and subsequent updates , or
- by querying the base registers for each transaction.
- If it detects a mismatch between reference data and reality, implement a data complaint against the data editor
- Do not request the data held in the registers from the right holder
Editorial AIS
Systems whose data is published by ISZR composite services. Composite services are ISZR services that provide data maintained in WR editorial systems with a link to reference data maintained in the WR:
- Population records - AISEO (administered by the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic)
- Agenda Information System of Foreigners - AISC(Administrator is the Police of the Czech Republic)
- Travel documents register - AIESCD (Administered by the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic)
- Registration of ID cards - AISEOP (Administrator is the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic)
- Information System of the Cadastre of Real Estate - ISKN (Administered by the Czech Office of Surveying and Cadastre)
- Territorial Identification Information System - ISÚI (Administered by the Czech Geodetic and Cadastral Office)
- AIS Competence - AISP (Administrator is the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic)
- eIdentity - (administered by the Ministry of the Interior of the Czech Republic)
Each ZR has its own editors who edit the data. The editors enter the data into the individual ZRs and together with the subject administrator of each of the editors, this keeps the data in the ZR correct and up-to-date. A data reclaim mechanism is used to ensure that the data is up-to-date and correct. Editors edit the data in the ZRs using their editing information systems based on the procedural execution of the agenda, which determines whether the execution exists in the file service or separate document registers in accordance with the legislation.
The reader may draw non-reference data in the form of so-called composite services. Since only current data that are correct and guaranteed by the State are found in the CR (except for non-reference data held in the basic registers), other non-reference data (e.g. historical data on the subject of the law or other useful data not found in the CR) can be retrieved from the editors' editing systems as part of the composite services.
Information on composite services is available at the SZR website.
eGovernment Service Bus / Shared Service Information System
The eGovernment On-Line Service Bus (eGSB), also known as the Information Shared Service System (ISSS) according to the legislative wording, is a unified interface for sharing data between different public administration information systems. It is part of the reference interface allowing individual AIS to draw on and publish data held on individual legal entities. Where an agency is required by law to maintain its own data records, it is obliged to publish its data to other agencies through eGSB/ISSS as a secure, standardised and documented interface for authorised readers. It is managed and operated by the Basic Registries Administration. The eGSB / ISSS interface allows:
- Publish services for sharing data relating to specific subjects and objects of law
- Use data sharing based on published services
- Translation of agency identifiers of individuals for whom data is exchanged between agencies (AIFO translation)
- Exchange of data files with data on subjects based on pseudonymised identifiers in relation to translated AIFO identifiers
- Provision of claim, notification and update services for data provided by AIS services
- Provision of independent auditing of the data exchange (stores information identifying the query and response and the technical cryptographic fingerprint of the message - hash)
In eGSB/ISSS there is a restrictive condition for the use of the MapAIFO element compared to ISZR. This element can only contain a single AIFO when called by G1:gsbCtiData and G11:gsbZapisData. There may be more than one AIFO in the response. This is because
eGSB/ISSS is fundamentally a multi-source system. A single context can be published by multiple publishers/AIS and the reader does not need to know in which one the information about the individual is located. ISSS performs a logical search, using ORG to identify target AISs (they maintain the AIFO and publish the context) and then sends a request to these publishers. At the same time, the eGSB/ISSS must not alter the payload of the message in any way, i.e. it cannot "split" and send one at a time to different targets. The above applies to all calls for now, but a so-called multi-source to single-source narrowing method is planned. That is, if the target AIS is uniquely identified, and thus known to the user of G1:gsbCtiData or G11:gsbZapisData. This would remove the requirement for a single AIFO only for the narrowing method on the target AIS.
The functionality of the principle is verified on the reference data held in the basic registers, where the client does not have to prove these data and their changes, but the whole public administration obtains these data through ISZR services and then makes decisions based on them. The principle of data sharing via eGSB / ISSS is only an extension of this functional unit to include other data.
Two main roles are defined for the use of eGSB / ISSS:
| Role | Description | What it provides |
|---|---|---|
| Publisher (provider) | ISVS administrator from which data is provided | Services publishing data via eGSB / ISSS, based on the agenda providing data from the AIS |
| Reader (user) | OVM retrieving data from another agenda based on its permission in RPP | Connection to eGSB / ISSS and calling publisher services (even multiple AIS of a given agenda), AIFO translation from the provider's agenda is used, the reader calls according to the AIFO of its agenda in case of a natural person. No translation is used for a legal entity. |
In the context of data sharing via eGSB / ISSS, the following aspects apply:
- The data are reported in the register of rights and obligations as data processed by the agenda on the basis of a legal mandate.
- The data must be held in the AIS
- The data is clear how it was created, who is responsible for its entry, changes and management, in which AIS it is held and how it can be amended or cancelled.
- The data provider is always the administrator of the AIS in which the data is held and recorded.
- The data is always linked to a right subject or right object in ZR.
- It shall be possible for the right holder to extract the data as an extract from the public administration information system.
As the aim is to link data efficiently and effectively, primarily to reduce the need for the client to prove facts, the data will be retrievable by the public authority:
- on the basis of the consent of the right holder (on behalf of the right holder), or
- on the basis of a legal mandate to keep the data in an agenda with a drawdown flag in RPP (ex officio)
Information on the data sharing information system is available at MoI website, including documents:
List of eGSB / ISSS services
| Code | Detailed description of the service | Version |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | gsbCtiData | 1.00 |
| G2 | gsbCtiZmeny | 1.00 |
| G3 | gsbVlozOdpoved | 1.01 |
| G4 | gsbVlozSoubor | 1.00 |
| G5 | gsbCtiSoubor | 1.00 |
| G6 | gsbVypisFronty | 1.00 |
| G7 | gsbOdpovedZFronty | 1.00 |
| G8 | gsbSmazatFrontu | 1.00 |
| G9 | gsbProbe | 1.00 |
| G10 | gsbCtiKontexty | 1.00 |
| G11 | gsbZapisData | 1.03 |
| K1 | katCtiSluzby | 1.00 |
| K2 | katCtiDetailServices | 1.00 |
| K3 | katCtiPrilohu | 1.00 |
| K4 | katCtiEndpoint | 1.00 |
Context eGSB / ISSS
Each agenda is defined by the relevant legislation. Within the agenda, the data necessary and specific for its execution are kept on subjects and objects. These data can also only be recorded on the basis of the relevant legal provisions. Subjects and objects are dealt with within an agenda in a certain context (given by legislation), i.e. subjects and objects are understood in a certain 'context' within the performance of that agenda. These contexts differ in the execution of different agendas, which is reflected, inter alia, by the fact that different objects are dealt with in relation to subjects in different agendas and different data are recorded and, where appropriate, exchanged on subjects and objects. We can therefore say that the context:
- determines the legal status of the entity (subject or object) within the agendas and
- the specific data (attributes) of the entity defined in the agenda are associated with it.
Methodologies for creating contexts address the detailed process
The context creation methodology introduces two levels of context - technical and conceptual. The technical level of context consists of an XSD schema that defines the syntax of the XML messages in which the shared data is expressed. In particular, to use eGSB/ISSS services for a linked data pool, it is necessary to know:
- The agency from which the reader wants to use the data,
- The agenda that the reader is executing and in which the data is read,
- The context for querying the data from the publishing AIS.
Before using eGSB/ISSS, the reader must first determine the context and its XSD schema according to which it will receive query responses in the eGSB/ISSS services. Therefore, he must first call a special eGSB/ISSS service to read the Context Catalog, in which he then finds out which context he must call to get the data from the providing agenda.
Conceptual Context Models
The conceptual level of a context consists of a conceptual model that defines the semantics (meaning) of a context by describing its semantic (meaning) links to other contexts maintained within the same agenda, as well as in other agendas, and by describing its semantic links to the public administration ontology. The ontology of public administration defines the basic concepts of public administration that exist across the legal order of the Czech Republic and the semantic links between them. Examples of such concepts are subject of law, object of law, natural person, legal person, etc.
The ambition of the conceptual model of the context is not to model the real world, but its abstraction describing the subjects and objects of data, data about them and the relationships between them as they are defined in the legislation and as they are understood in the given agenda. The conceptual model is derived from the general meanings defined in the ontology of public administration, it takes over, specialises and extends these and redefines them if necessary. The elements of the conceptual model are linked to the corresponding legislative provisions from which they derive. As the conceptual model of context is linked to the conceptual models of related contexts and to the ontology of public administration, it is itself an ontology. The set of conceptual models of all contexts then forms an ontology describing
- the subjects and objects of law,
- the contexts in which they exist,
- the data held about them in the contexts
- the semantic relationships between them
This forms a conceptual semantic map of the data held by the public administration.
List of contexts
A detailed list of contexts is available at https://egsbkatalog.cms2.cz/. This list is only available from the CMS/KIVS network, not from the public internet.
| Order | Code | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A1029.1 | Insured |
| 2 | A1029.2 | Self-employed |
| 3 | A1029.3 | Employer |
| 4 | A1029.4 | Territorial organizational unit |
| 5 | A1046.1 | Driver's licence holder - documents for applying for a driving licence |
| 6 | A1046.2 | Driver - application for driving licence |
| 7 | A1046.RidicRozsirene | Driver - extended data |
| 8 | A1046.RidicBasic | Driver - basic data |
| 9 | A1046.RidicBasic | Driver - basic data |
| 10 | A1061.1 | NBU Avizace |
| 11 | A121.1 | Authenticated Person Data Overview |
| 12 | A121.2 | List of business entity data |
| 13 | A124.1 | ISKN - Record of rights for a person |
| 14 | A124.2 | ISKN - Certificate of Ownership |
| 15 | A1341.1 | Insurer's Certificate of Insurance |
| 16 | A1341.2 | OSVC PP notice |
| 17 | A1341.3 | OsVC PP ZP notification |
| 18 | A1341.4 | List of OSVC PP |
| 19 | A344.1 | Notification via Citizen Portal |
| 20 | A3726.1 | Patient |
| 21 | A385.1 | Notification of OSVC PP |
| 22 | A385.2 | List of OSVC PP |
| 23 | A392.1 | Debtor |
| 24 | A392.2 | ODU |
| 25 | A4003.1 | Health Service Providers |
| 26 | A4003.2 | Patient medical records |
| 27 | A418.1 | Person under investigation |
| 28 | A418.2 | Vehicle under investigation |
| 29 | A418.3 | NBU Lustration |
| 30 | A483.1 | Criminal Records Bureau |
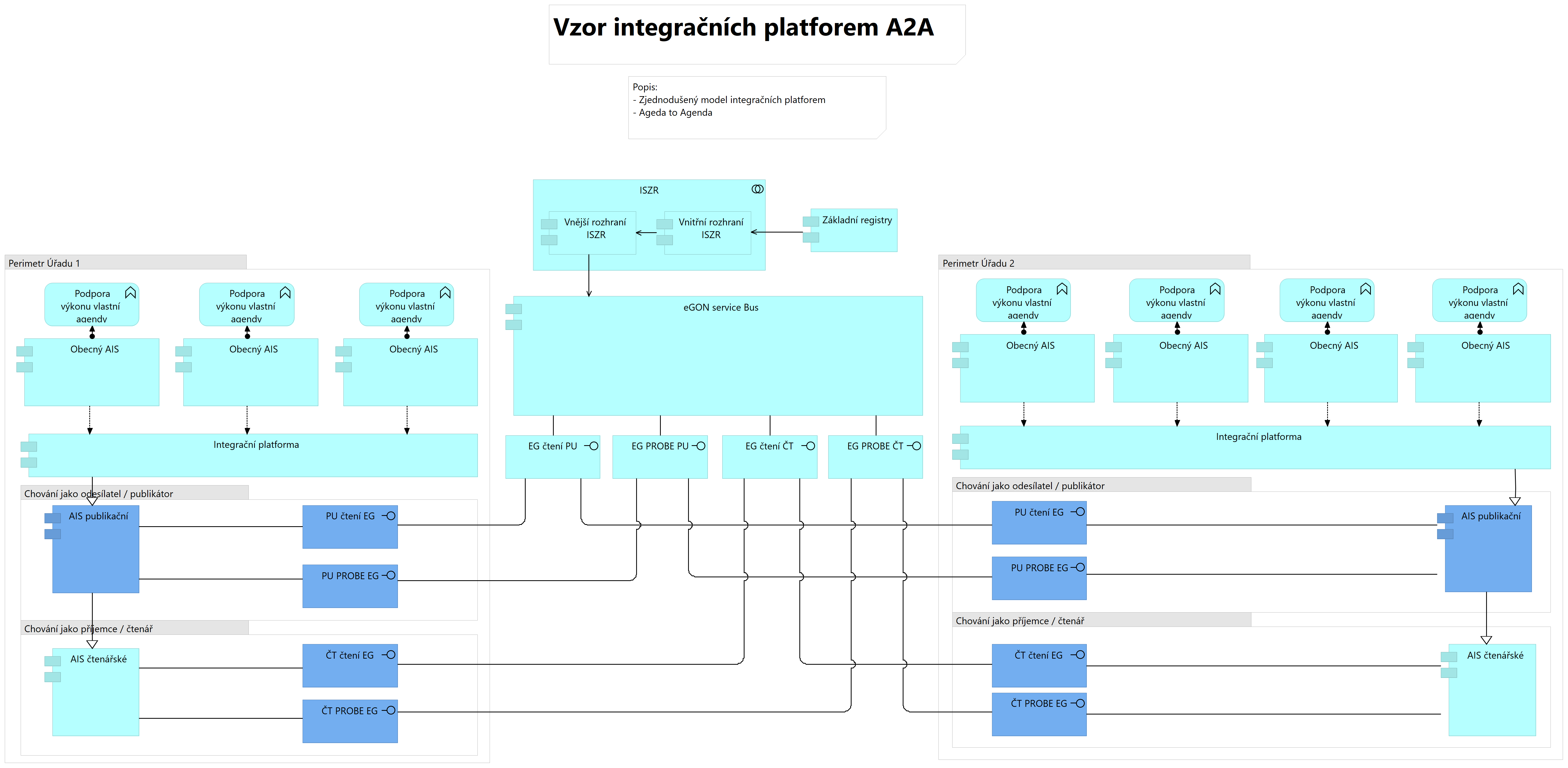
A view of the integration platform interconnections
IS Interface for Batch Data Exchange
The Form-based AIS (FAIS) is a component of ISZR, which, through special form-oriented services, allows to request the release of multiple data from the basic registers and subsequently mediates the batch release of these bulk data through data boxes. It is used for cases where there is a legal mandate to use reference data in multi-subject groups. This is the case, for example, for voters' list issues.
FAIS is also used to handle the output of basic register data in the form of form requests to the SZR data box and responses to the applicant's data box. For example, requests for data extracts, data usage reports, etc. are handled in this way. FAIS has an interface to document management filing service according to National Standard for Electronic Filing Systems
FAIS therefore provides, among other things:
- Voter lists provided to municipal election authorities
- Issuance of bulk batches of data according to the permissions in the relevant agenda
- Execution of the right holder's request for an extract of data from the systems connected to the reference interface, i.e. the entire PPDF
- Compiling a summary of the extract of data usage sent to the data box of the right holder
FAIS operates according to the following points:
- A data extract request is made by the applicant and sent as a form to the FAIF.
- FAIS, as a component of the ISZR, retrieves the data message with the request form and processes the request, verifying data permissions and the release of individual data
- After using the services of the ISZR, FAIS compiles the response and sends it back to the applicant's data box in the given format.
The FAIS is not primarily intended for use by agency information systems, but for processing form requests authenticated by the identity of the sender of the request via their data box. The ISR External Interface Services is used by the agency information systems to use the output of the basic registers.
FAIS will provide the corresponding data extraction process via data boxes for all data published on the PPDF.
Reference Interface Rules
Method of obtaining reference data
Web Services
Through the web services, an entity can draw reference data from the RoW. An entity that operates in an agenda, has this agenda duly declared in the RPP, has registered its agenda information system (also known as AIS) and has been issued a valid certificate by the administration of the basic registers (also known as SZR), and must have its own legal authorization to draw data in its own law and according to Law No.111 /2009 Coll., on the basic registers, this entity is entitled to draw reference data from the ZR through external services of the information system of the basic registers administration (also referred to as ISZR).
In order to retrieve the reference data by web services, it is necessary to first identify your data trunk to the CR and then log in to receive notifications of changes.
- For information on the RoW, see: http://www.szrcr.cz/vyvojari
- Information on how to connect your AIS to the ISZR: http://www.szrcr.cz/file/170/
- Information on how to use notifications from the ZR can be found here: http://www.szrcr.cz/spravny-postup-prace-s-notifikacemi-a-udrzovani-datoveho
- Information on the description of the ZR services: http://www.szrcr.cz/file/175/display/
- Detailed description of the ZR services: http://www.szrcr.cz/vyvojari/podrobny-popis-egon-sluzeb-zakladnich-registru
Czech POINT
The abbreviation Czech POINT stands for Czech Submission Authentication and Information National Terminal. It is a contact point of public administration that provides citizens with, in particular, verified data held in central registers such as the Criminal Register, the Commercial Register or the Trade Register. In addition to standard services, extracts from the basic registers can be used pursuant to Act No 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended. Citizens have the opportunity to verify the data held in the registers about them, while officials have access to reference data from the basic registers through forms in the CzechPOINT@office section.
One of the objectives of the implementation is to make services to citizens and other entities faster, more accessible and more efficient. Czech POINT is thus a contact point of public administration, which allows to obtain statements or make submissions in a single place.
- Information on Czech POINT can be found at http://www.czechpoint.cz/public/
Data Box Information System
The datový boxes can be used to send documents in electronic form to public authorities and to receive them from them.
The Communication via data boxes replaces the classic method of delivery in paper form, because Act No. 300/2008 Coll., on electronic acts and authorised conversion of documents, puts the paper and electronic versions of the sent document on an equal footing. Public authorities and legal entities are automatically provided with data boxes, all others upon their request. Anyone who has a data box and is an authorised person pursuant to Article 8 of Act No 300/2008 Coll., on electronic acts and authorised document conversion, as amended, may request extracts.
- Information on data boxes can be found at https://www.datoveschranky.info/
Citizen's portal and public administration portal
Natural persons (citizens) have the possibility to request extracts from the basic registers via a data box on their personalised citizen's portal account if they have a data box set up on the citizen's portal and connected to their profile. It is possible to log in to the citizen portal with a data box, name-password-SMS or electronic ID card with chip, issued from 1 July 2018.
- Information on how to log in https://obcan.portal.gov.cz/prihlaseni
- Information on electronic identity https://obcan.portal.gov.cz/prihlaseni
- It is also possible to request an extract from the ZR via the public administration portal.
- Link to individual forms can be found here: https://www.portal.gov.cz/obcan/formulare
Who can request reference data from the CR
Web services
A public administration entity with its AIS, which has a legal mandate in its law to use reference data from the FR, operating in a duly declared agenda in the Register of Rights and Obligations and has been issued a valid certificate by the administration of the basic registers to access the FR. Furthermore, a private law entity indirectly through the AIS of a public authority, which again has a legal mandate to use data from the basic registers in the assigned agenda duly declared in the RPP.
Czechpoint
The contact point, depending on the type of individual forms available within Czechpoint, can be used by individuals, natural persons and legal entities. Further information on who can apply for each type of form is available in Types of applications for obtaining reference data from the ZR.
Data Box Information System
The Data Box Information System is a means for obtaining reference data from the basic registers by sending one of the forms in Types of requests for obtaining reference data from the basic registers Anyone who has an established data box and is an authorised person pursuant to Section 8 of Act No. 300/2008 Coll., on Electronic Acts and Authorised Conversion of Documents, as amended, may request extracts. Other subjects may optionally set up a data box.
Citizen's portal and public administration portal
Any natural person (citizen) who has a data box connected to his/her profile on his/her personalised account on the citizen portal is able to request an extract of data from the basic registers within the citizen portal. Within the public administration portal, any subject listed in the Types of requests for obtaining reference data from the basic registers, according to the type of request has the possibility to submit a request for obtaining reference data from the basic registers.
Types of requests for obtaining reference data from the RoW
Request for extraction of data from the population register - pursuant to Section 58 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
- The request may be submitted by the subject (natural person) about whom the data is kept.
- A legal representative may apply on behalf of the subject of the right pursuant to Section 58(9) of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
- A proxy may apply on behalf of the subject of the right on the basis of a power of attorney with an officially certified signature of the proxy.
Application for public extract of data from the register of persons - pursuant to Section 61 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
- The application may be submitted by any natural person (does not have to be a subject of law).
- The request may be made for the provision of data on any natural person, legal entity or public authority.
- All data will appear in the extract as in the non-public extract (see below) except for personal data of persons who are linked to the population register.
Request for extraction (non-public) of data from the register of persons - pursuant to Section 61 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
- The request may be submitted by a subject (an entrepreneurial natural person or a statutory body of a legal person), about whom the data are entered in the register of persons.
Application for record of the use of data in the population register - pursuant to Section 14 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
- The application may be submitted by the subject (natural person) about whom the data are entered in the population register.
- In the application, the subject shall indicate the period for which the record is to be provided.
- Every natural person who has a data box will receive a free of charge Record on the use of data in the population register automatically in the data box for the past calendar year, in accordance with Article 14(4) of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
- For information on how to read the record of data use, please refer to the practical guide: see http://www.szrcr.cz/obcan-a-podnikatel
Request for record of data use in the register of persons - pursuant to Section 14 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on basic registers, as amended.
- The request may be submitted by the subject (an entrepreneurial natural person or the statutory body of a legal person) about whom the data are kept.
- In the request, the subject shall indicate the period for which the record is to be provided.
- Each entrepreneurial natural and legal person who has established a data box shall receive a free of charge Record on the use of data in the register of persons automatically in the data box for the past calendar year, in accordance with Article 14(4) of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
Request for change of data in the event of a discrepancy in the population register - pursuant to Section 14 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
- The subject of the right (a natural person) may apply for a change of data when a discrepancy is found in the population register.
- On the basis of the request, a proposal for changing the reference data kept on the subject of the right in the population register will be submitted.
- If the reference data is changed, the natural person who has a data box will receive a free of charge List of reference data automatically in the data box, in accordance with Section 14(5) of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
Request for change of data in case of a discrepancy in the register of persons - pursuant to Section 14 of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
- The subject of law (an entrepreneurial natural person or a statutory body of a legal person) may apply for a change of data upon discovering a discrepancy in the register of persons.
- On the basis of the request, the applicant submits a proposal to change the reference data kept about the person in the register of persons.
- A natural person in business or a statutory body of a legal person may apply for a change of data in case of a discrepancy in the register of persons.
- If the reference data is changed, every entrepreneurial natural or legal person who has a data box will receive a free of charge Extraction of reference data automatically in the data box, in accordance with Section 14(5) of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the Basic Registers, as amended.
Request for provision of data from the population register to a third party - pursuant to Section 58a of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on basic registers, as amended.
- On the basis of the request, the subject of the right (natural person) provides his/her data to another natural or legal person.
- It is possible to provide them with all or selected data kept in the population register.
- It is not necessary to provide your data to a public authority in this way, as it is obliged to find out the reference data.
Request for revocation of the provision of data from the population register to a third party - pursuant to Section 58a of Act No. 111/2009 Coll., on the basic registers, as amended.
- On the basis of the request, your data will no longer be provided to another natural or legal person. The previous consents to the disclosure of data to a third party selected by you and made by the request above will be revoked.
Fees associated with requests for extracts
- Citizen Portal and Public Administration Portal - Submission of requests by data box using the forms published on the Citizen Portal and Public Administration Portal and the issue of extracts is free.
- Czech POINT - requests submitted through the Czech POINT public administration contact point are charged, however, submission of requests for change of reference data and provision/revocation of provision of reference data to a third party are free.
Obligation to use the reference interface
The obligation to use reference interfaces for making so-called "links" between different public administration information systems is imposed by the Act on Public Administration Information Systems. Thus, in general, it is the reference interface that is to be primarily used for data sharing, data exchange and interconnection of individual public administration information systems of different administrators. For information systems of the same administrator, this may not always be the case, unless the translation of agency identifiers is used for communication about a legal entity within two or more agencies.
It must be stressed that only by using the reference interface is the translation of AIFOs correctly performed (the AIFO of one person in one agency must not be provided to another agency). Only the reference interface is linked to the ORG registry and performs the translation of the AIFO.
Possibility to use the reference interface
In addition to the obligation for public administration information system administrators, there is also the possibility for other entities to use the reference interface or the services it provides. Specifically, these are entities of the type of SPUU (Private Data User) according to Act 111/2009 Coll., which need a legal authorisation to use the services of the reference interface.
Use of the reference interface for the exchange of data within the interconnected data fund
The exchange/sharing of data between the different public administration information systems is carried out exclusively through the reference interface, namely the eGSB/ISSS component. As specified in linked_datovy_fund, the data exchange is always realised within a per-entity context.
Access to the services of the reference interface is only possible at the network level through the Central Point of Service (CMS), and consequently to the communication infrastructure of public administration (KIVS), which can be called a private network for the performance of public administration on the territory of the state.
Administrators of agency information systems must implement the connection to the reference interface, according to the relevant methodological documents and operating rules:
Use of the reference interface for reference data retrieval
In addition to the operating rules, administrators of agency information systems follow other procedures, mainly legislative ones. The current state (2020) still forces a legal mandate for the use of reference data. V
Use of the reference interface for the provision of agency data
Administrators of agency information systems providing agency data implement the connection of their AIS to the eGSB/ISSS in the role of publisher and control the permissions to use the data according to the permissions in RPP. For data exchange, they shall build their AIS services to be called and mediated by eGSB/ISSS.
Use of the reference interface to draw on agenda data
Administrators of AISs that use data provided by another agency make calls to eGSB/ISSS services (they do not need to know the specific AIS, they request the data from the agency), and only if they have the appropriate permissions registered with the provider agency in RPP.
Use of the reference interface when registering and editing data in basic registries
The Basic registers reference data editors implement the connection of their editorial agency information systems to ISZR by means of external interface services according to the relevant documentation of the Basic Registers Administration and, in cases where the agency information systems are not also separate document registers, then the connection of these systems to eSSL within internal links. They do not use any other interface than the ISZR for editing data and handling complaints about data in the basic registers.

Discussion